What is thin-wall plastic parts?
Thin-wall plastic parts not only depend on the thickness of the plastic part, also on the flow length to thickness ratio of the plastic and the viscosity coefficient of the plastic. It can be divided into the following three situations:
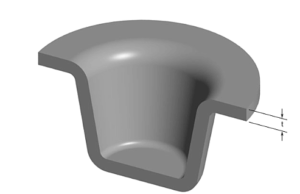
1. The ratio of flow length to thickness (L/T) above 150 is thin-wall injection molding. Flow length refers to the longest distance from the melt entering the mold to completely filling the cavity.
2. The thickness of the plastic part is less than 1mm, and the projected area is above 50cm².
3. For disc-shaped plastic parts, the thickness/diameter ratio of less than 0.05 can be defined as thin-wall plastic parts.
The flow length to thickness ratio of commonly used plastics.
LDPE 270 ; HDPE 230 ;PP 250;PS 210;ABS 190;PC 90;PA 170;POM 150;PMMA 150;TPE 150.
Good fluidity plastics such as PP, PS and PE with a viscosity coefficient of 1. When the wall thickness is less than or equal to 0.5mm or the L/T ratio is greater than 150, it is a thin-walled plastic part.
For plastic parts with poor fluidity, the wall thickness should be divided by the viscosity coefficient N. The flow length to thickness ratio of plastic parts should be L/T*N. For example, a cell phone battery case made of PC material has a flow length L=40mm, a thickness T=0.4mm, and a viscosity coefficient N=2. Its flow length to thickness ratio (L/T*N=200).
The table is viscosity coefficient of thermoplastic:
| Number | Thermoplastic | Viscosity Coefficient | Fluidity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PE,PP,PS | 1 | Good |
| 2 | NYLONS,POM | 1.2-1.4 | Medium |
| 3 | Cellulose Plastic | 1.3-1.5 | |
| 4 | ABS,AS,MBS | 1.3-1.5 | |
| 5 | PMMA | 1.5-1.7 | |
| 6 | PC,Rigid PVC,PES,PSF,PPO | 1.7-2.0 | Bad |
Advantages of thin-wall plastic parts:
- Save plastic ,lower the cost
- Reduced molding times
- Can leave more space for the product,easy to use.
Shortcoming of thin-wall plastic parts:
- Poor stiffness
- Molding is difficult
- Complicated process
Thin-wall plastic parts design points
Thin-walled plastic parts have small wall thickness, but they must meet the impact strength, appearance quality and dimensional stability of the product, as well as the tolerances of precise dimensions, and they can withstand large static load requirements. Therefore, the rigidity, impact resistance, and manufacturability of plastic parts must be considered in the design process.
- Since the thin-walled plastic injection mold cavity is very narrow and the melt filling resistance is large, the plastic parts should be designed to avoid sharp corners and reduce perforation.
- Thin-wall injection molding processes use higher pressures, which can limit localized contraction, thus allowing thicker stiffeners to be designed. When the wall thickness is less than 1.00mm, the ribs can be as thick as the wall.Also provided may be added in small bead on the outer edge of the interior moldings or plastic parts.
- Since the shrinkage of the thin-walled plastic parts is small, the draft of the reinforcing ribs, bosses, and edges should be increased.
- Since the flexural stiffness is inversely proportional to the cube of the wall thickness, the thinner the part, the poorer the stiffness. The easiest way to increase the stiffness of plastic parts is to use fiber-filled reinforcements. Fastening of plastic parts is achieved by means of snap connection, screw connection, ultrasonic welding, and two-color injection molding in combination parts in order to connect multiple parts together as firmly as a single part.
- The last factor to consider is the impact strength. Most thin-walled plastic parts have strict impact resistance requirements, because the product will have uncontrollable events during use. There are two ways to increase the impact strength:
- Transfer shock load. The load can be transferred to the internal structure of the plastic part. This way does not require extra space and therefore the shape does not deform. It should be noted that consideration should be given to avoid stress concentration points.
- The exterior is designed to absorb most of the impact through deformation. This design requires more space to protect the internal plastic parts from damage. Stress concentrations such as sharp gaps in the structure should be avoided.
Selection of plastics
At present thin-walled plastic injection molding applications more plastic: PP, ABS, PC / ABS mixture and PA6 and so on. PP plastics have a MI of up to 60g/10min, such as Basell’s Moplen RP1086. The reason why many plastic parts use PC/ABS is the toughness of PC and the fluidity of ABS, which are often used in thin-walled plastic parts.

Injection molding machine selection
Experience tells us that conventional injection molding machines can hardly satisfy thin-wall injection molding.
- Thin-wall injection molding machines generally require smaller barrels than conventional injection molding machines. The injection volume is preferably 35%-75% of the maximum injection volume of the injection molding machine.
- Injection molding machines must use high-resolution microprocessors to control. Throughout the thin wall injection molding process. Pressure and speed should be controlled independently at the same time. The conventional way of injection molding machine is to use the speed control during the filling stage and the pressure control stage to pressure control. This way does not apply.
- The hydraulic injection molding machine for thin-wall injection molding machines is designed with an accumulator, which can frequently drive injection and mold clamping. In order to withstand the high pressure of the injection molding machine, the lock plate force force must reach 7.5~10.5kg/mm^2. In addition, when the wall thickness reduces the injection pressure, the large template helps to reduce the bending.
- Speed is one of the key factors for the successful injection of thin-walled plastic parts. Rapid filling and high pressure can inject molten thermoplastic material into the mold cavity at high speed to prevent the gate from solidifying. If a standard plastic part is filled within 2 seconds, then the mold thickness is reduced by 25%, then the filling time needs to be reduced by 50%, just 1s.
In this article we have written about thin-walled plastic parts. The definition of thin-walled plastic parts, the advantages and disadvantages of thin-walled plastic parts. How to choose raw materials, how to choose the injection molding machine. There are also design requirements for thin-walled plastic parts. I hope this content will help you. In the following articles we will write some design experiences and some examples of thin-walled plastic injection molds.
